In the dynamic world of finance, understanding interest calculation methods is crucial for both individuals and businesses alike. Whether you’re taking out a loan, putting money in a savings account, or engaging in complex financial transactions, comprehending how interest is calculated can significantly impact your financial decisions.
In this article, we’ll delve into the various interest calculation methods and explore how banks calculate interest on savings accounts, mortgage loans, while also shedding light on how real estate developers calculate interest on delayed payments, a process known as the product method and how eBuildAuto Real Estate CRM Software for developers help in simplifying the complex process.
Table of Contents
ToggleInterest Calculation Methods:
1. Simple Interest:

Simple interest is the most straightforward method of interest calculation, commonly used for short-term loans or investments. It’s calculated based solely on the principal amount of a loan or investment. The formula for simple interest is: Interest = Principal × Rate × Time. Here, the rate refers to the annual interest rate, and time represents the time period for which the interest is calculated.
2. Compound Interest:

Compound interest is a more complex but widely used method of interest calculation, especially for long-term investments and loans. Unlike simple interest, compound interest takes into account both the principal amount and the accumulated interest from previous periods. As a result, interest is calculated on the total amount (principal + interest) rather than just the principal.
Compound interest can be calculated using the formula: A = P(1 + r/n)^(nt), where A is the future value of the investment/loan, P is the principal amount, r is the annual interest rate (in decimal), n is the number of times interest is compounded per year, and t is the time the money is invested or borrowed for, in years.
3. Amortization:

Amortization is primarily used for loans, such as mortgages. It involves paying off a loan with regular payments over a specified period.
With amortizing loans, each payment is divided into two parts: one portion goes towards reducing the principal amount owed, while the other portion covers the interest accrued. As the loan matures, the proportion of each payment allocated to interest decreases, while the portion allocated to the principal increases.
4. Nominal Interest Rate vs. Effective Interest Rate:
It’s crucial to distinguish between the nominal interest rate and the effective interest rate. The nominal rate is the stated annual interest rate without considering compounding.
Conversely, the effective interest rate reflects the actual interest earned or paid, accounting for the effects of compounding. The effective interest rate is generally higher than the nominal rate for investments and lower for loans.
How Banks Calculate Interest on Savings Accounts:

When it comes to saving accounts, banks typically use compound interest to calculate the interest earned on deposits. The frequency of compounding varies among financial institutions but is commonly done on a monthly or daily basis. Here’s how banks calculate interest on saving accounts:
- Annual Interest Rate: Banks set a percentage representing interest earned annually.
- Compounding Frequency: Determined by the bank, interest may compound monthly or daily.
- Interest Calculation: Using the compound interest formula with principal, rate, and compounding frequency.
- Interest Crediting: Earned interest is credited to the account at each compounding period’s end.
- Continuous Growth: Account balance increases over time due to deposits and accumulated interest.
“Real Estate Developers interest calculation – the Product Method!”

When real estate developers sell properties, most of the buyers pay in installments or through financing. However, sometimes buyers may default on their payments or delay them beyond the agreed-upon time frame. This delay can have financial repercussions for the developer, as they may have ongoing expenses and financial obligations that need to be met.
In such cases, they apply a method known as the product method to calculate interest on the outstanding amount. The product method involves multiplying the outstanding amount by a predetermined interest rate and the number of days the payment is delayed from the due till the receipt of amount.
This is a continuous process until the final payment is received.
Basic Terminology:
1. Due Amount: The construction of a building happens in stages, milestones or slabs. Each stage has a particular percentage which the buyer has to pay as the work progresses.
2. Outstanding Amount: The outstanding amount refers to the payment that the buyer has failed to make on time or past the due date or has delayed.
This could include instalment payments, down payments, or any other outstanding balances owed by the buyer to the developer.
3. Predetermined Interest Rate: Real estate developers typically establish a predetermined interest rate that will be applied to the outstanding amount for each day it remains unpaid.
This interest rate is often outlined in the sales agreement or contract between the developer and the buyer. It is designed to reflect the opportunity cost incurred by the developer due to the delayed payment.
 FYI : According to RERA rules, the rate of interest applicable for delayed payments is typically set at 2% above the State Bank of India’s marginal cost of lending rate (MCLR). As of the current context, with the State Bank of India’s MCLR standing at 8.05% per annum, the prescribed rate of interest for delayed payments under RERA would be 10.05% per annum.
FYI : According to RERA rules, the rate of interest applicable for delayed payments is typically set at 2% above the State Bank of India’s marginal cost of lending rate (MCLR). As of the current context, with the State Bank of India’s MCLR standing at 8.05% per annum, the prescribed rate of interest for delayed payments under RERA would be 10.05% per annum.
4. Number of Days Delayed: The product method takes into account the number of days that the payment is delayed beyond the due date. This duration is essential in determining the total interest accrued on the outstanding amount.
Once these factors are determined, the real estate developer can calculate the interest owed using the product method.
Example of Interest Calculation:
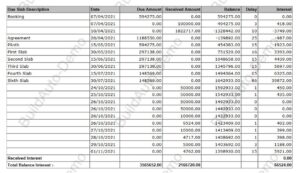
Let’s understand with an example of interest calculation generated through eBuildAuto CRM Software:
In the example, the report is generated as of 16/11/2021, with an interest rate of 10.30%.
1. Booking Amount: Rs. 5,97,275.00, due on 07/04/2021. A payment of Rs. 1,00,000.00 is received on the same date, leaving a balance of Rs. 4,94,275.00. The interest amount is Rs. 418, calculated as 4,94,275 x 10.30% for 3 Days (from 07/04/21 to 10/04/21).
2. Next Receipt: Rs. 18,22,717.00 received on 10/04/21. After deducting Rs. 4,94,275 from Rs. 18,22,717, the balance is Rs. -13,28,442. As the customer has paid excess, the system calculates a negative interest of Rs. 3,749 for 10 Days (from 10/04/21 to 20/04/21).
3. Next Due Agreement Amount: Rs. 11,88,550.00, due on 20/04/2021. The amount received is excess (Rs. 11,88,550 – Rs. 13,28,442 = -1,39,832), resulting in a negative interest of Rs. 978 for 25 Days.
4. Next Due for Plinth: Rs. 5,97,275.00, with a remaining balance of Rs. 4,54,383.00 after deducting excess amount. The due balance is for 15 days, resulting in interest calculation.
The final interest calculated is Rs. 66,524 as of 16/11/2021.

Note: The calculation is purely on the balance at any given stage or after the receipt of the amount on a particular stage. If the customer has paid excess, the negative interest is not displayed on collection letters (i.e., demand, reminders, etc.).
These calculations are almost impossible or too time-consuming if done manually. eBuildAuto Real Estate CRM does this accurately and within a few seconds.
By using the product method, real estate developers can mitigate the financial impact of delayed payments and ensure that they are fairly compensated for their time and resources. Additionally, it serves as a deterrent against late payments, encouraging buyers to fulfill their financial obligations promptly.
In summary, eBuildAuto’s real estate crm software, interest calculation feature is one the most valuable tool for real estate developers to calculate interest on delayed payments. It helps them recoup financial losses associated with delayed payments and reinforces the importance of timely payments in real estate transactions.
================================================================
Must Read :
7 Ways eBuildAuto Real Estate CRM Software Simplifies Collections
================================================================